AAC
An audio file format, standing for Advanced Audio Coding. We recommend using MP3 instead of AAC for the greatest compatibility across all listening apps.
Baked in
This refers to part of the show, for example, an introduction or advert, that is recorded in the original episode and is heard by all listeners. This typically can’t be changed without editing and re-uploading the whole episode audio file.
Bed
This normally refers to music or audio that plays in the background while someone is talking on the podcast.
Bit Depth
Technically, the audio bit depth determines the number of possible amplitude values we can record for each audio sample.
In real-world terms: Along with Bit Rate/Sample Rate, the Bit Depth of your recording sets the maxim possible audio quality. Common Bit Depth settings are 16, 24, and 32-bit, but for podcasting, 16-bit audio should be good enough.
Bit Rate
Along with Bit Depth, Bit Rate defines the maximum possible audio quality of your recordings. For podcasting, we recommend 96 kbps mono audio.
Clipping
Clipping occurs when the audio source is too loud, and the loudest parts are ‘clipped’ from the audio. This can sound like a glitch in the recording, and in extreme cases can even damage microphones. Where possible, turn down the recording volume sensitivity to avoid this.
Compression
When editing your audio, if you compress it, the loudest parts will be made quieter and the quieter parts will be made louder, effectively making the audio a more consistent volume throughout the recording. Some recording software allows you to run compression at the same time as recording rather than applying compression afterward.
Creative Commons (CC)
A non-profit organization that provides legal tools to give creators the ability to specify how their work may be used by others. CC licenses range from allowing any use with proper attribution to permitting only non-commercial sharing in unchanged form.
If you hear a piece of audio or music that you’d like to use, and it has a CC license, check the details of that license to make sure you’re allowed to use it.
Condenser Microphone
A condenser mic is a type of microphone that uses a capacitor to convert sound waves into an electrical signal. Known for their high sensitivity and wide frequency response, they are excellent for capturing detailed and accurate sound, often used in studio recording.
However, they require a power source, are generally more expensive, and can be less durable than other types, making them less suitable for rough handling or high-volume (loud) environments.
DAW
A Digital Audio Workstation (DAW) is a software application used for recording, editing, and producing audio files. DAWs provide a range of capabilities including multitrack recording, MIDI sequencing, audio effects processing, and mixing, making them essential tools for musicians, sound engineers, and producers.
Some common FREE examples to get you started: GarageBand, Audacity, Cakewalk
Directory / Directories
A podcast directory, often called a listening app or similar, is a listing or database of podcasts that users can browse or search to discover new podcasts. These directories typically allow users to search by various criteria such as genre, popularity, recent additions, or keywords. Some examples of popular podcast directories include Apple Podcasts and Spotify. Podcasters typically submit or publish their podcast to these directories using their show’s RSS feed.
Dynamic Insertion
Dynamic audio insertion or dynamic ad insertion in podcasting allows ads or other audio to be inserted into podcast episodes in a way that can be changed over time, instead of being permanently embedded in the recording. This allows ads to be targeted based on factors like the listener's location, the date, or user behavior, and enables podcasters to monetize both new and older episodes, or change introduction music at a later date etc.
Dynamic Microphone
Dynamic mics are more durable, can handle high sound pressure levels, and don't require a power source, making them ideal for live sound environments and loud instruments.
However, they typically have a less accurate frequency response compared to condenser microphones, which may result in less detailed sound capture, particularly for quiet or subtle sounds.
Dynamic Range
The difference between the quietest and the loudest parts of an audio signal. Striking a balance in dynamic range is important to keep the audio sounding natural while ensuring it's comfortable for listeners without constant volume adjustments.
Episode
A single podcast recording, released for example daily or weekly, typically focusing on a set topic or guest. Each podcast can contain multiple different episodes. Episodes can range from minutes to hours in length.
EQ
EQ (equalization) is a process that adjusts the balance of different frequency components in an audio signal. It's used to enhance the sound quality, make certain elements stand out, or minimize unwanted noises, making the podcast sound more clear and pleasing to the listener.
Gain
Audio gain refers to the increase or amplification of the level of an audio signal. In a way you can think of this as setting the sensitivity level of your microphone/recording equipment.
High-Pass Filter
A high-pass filter (HPF) is an audio filter that allows frequencies above a certain point to pass while reducing lower frequencies. It's used to remove low-frequency noise such as wind, rumble, and vibrations in a recording.
Podcast Host, Co-Host
This is the person or people who present the content of a podcast, leading conversations, interviewing guests, or narrating stories. They are the voices that the listeners hear and associate with the podcast.
Podcast Hosting Service
This is a service that stores and delivers podcast files to various listening apps and directories. A podcast hosting service provides the necessary infrastructure to make podcasts accessible to listeners around the world via the internet.
ZenCast.fm (that's us!) is a podcast hosting service.
ID3 tags
ID3 tags, also known as metadata, are embedded in digital audio files, storing information like title, artist, and album. In podcasting, they include details like episode title, podcast name, episode number, and host name, which podcast players display for easy navigation and understanding. Your DAW will allow you to fill in this information after editing your podcast.
Jingle
In podcasting, a jingle is a short, catchy tune used for introductions, transitions, or conclusions, helping to create a recognizable identity for the podcast.
Low-Pass Filter
A low-pass filter (LPF) is an audio filter that allows frequencies below a certain point to pass while reducing higher frequencies, often used to remove high-frequency noise found in phone or Skype interviews.
M4A File
An M4A file is an audio file format developed by Apple, providing better sound quality than MP3 at the same file size, commonly used for music and podcasts on Apple devices. Despite slight differences in quality, we heavily recommend uploading your final episodes in MP3 for wider compatibility.
Metadata
Metadata, also known as ID3 tags, are embedded in digital audio files, storing information like title, artist, and album. In podcasting, they include details like episode title, podcast name, episode number, and host name, which podcast players display for easy navigation and understanding. Your DAW will allow you to fill in this information after editing your podcast.
Mixdown, Mixing down
In podcasting, mixdown is the process of combining multiple audio tracks into a single file, blending together dialogue, music, and sound effects into the final audio file to be published as an episode.
Monetization
Monetization in podcasting refers to the various ways podcasters generate revenue from their content, such as through sponsorships, advertising, donations, subscription fees, or selling merchandise. For more information check out our help article on monetization.
Mono Audio
Mono audio, short for monophonic, refers to sound that is channeled through a single audio track, with the same signal sent to all speakers or headphones, unlike stereo audio which uses two distinct channels.
Most podcasts are fine in mono and don’t need stereo unless you want to showcase a lot of high-quality music.
MP3 File
An MP3 file is a digital audio file format that uses lossy data compression to reduce file size, widely used for storing and playing music and audio content.
We recommend using MP3 for all your podcast audio uploads.
Normalization
Audio normalization is the process of adjusting the overall volume of an audio recording to a standard level, ensuring consistent volume across different tracks or within a single track.
Peaking
Audio peaking is when the volume level of an audio signal reaches the maximum volume for that recording.
Some audio producers use this term the same way as ‘clipping’ , describing the audio going over the maximum volume limit, resulting in a harsh sound and potential equipment damage.
Podcast (or Show)
A podcast is a digital audio or video series available on the internet for downloading or streaming. Episodes can be automatically received by subscribers and typically feature discussions on a variety of topics, ranging from news and politics to hobbies and entertainment.
Popping / mic pop cover
Audio popping in podcasting refers to abrupt, sharp sound disturbances often caused by fast-moving air from plosive consonants ('p' and 'b') hitting the microphone, which can be minimized with a pop filter and proper microphone technique.
RSS feed
In podcasting, an RSS feed is a web feed that allows users and applications to receive regular updates of new podcast episodes in a standardized format. This feed is submitted to podcast directories/listening apps to allow listeners to subscribe and automatically receive new episodes.
Sample Rate
Audio sample rate is the number of samples of audio carried per second, measured in Hz or kHz (1 kHz = 1000 Hz). A higher sample rate means a higher quality audio file but also a larger file size. A common sample rate for audio is 44.1 kHz (CD quality), which we recommend for your podcast recordings.
Submitting a Podcast
To submit a podcast means to provide the RSS feed of your podcast to a podcast directory or platform (like Apple Podcasts or Spotify). Once submitted and approved, your podcast will be available on that platform for listeners to find, subscribe to, and download or stream episodes. Getting the podcast initially approved often takes a few hours or days, but after that’s done, new episodes you publish will typically be available in minutes.
Stereo Audio
Stereo audio refers to sound divided into two channels, typically left and right, creating a sense of direction or depth, providing a more immersive listening experience compared to mono audio. Typically you should use mono audio for a general podcast, and only consider stereo if you showcase a lot of high quality music.
Stinger/Sting
In podcasting, a stinger is a short sound clip or musical phrase used to punctuate a segment, indicate a transition, or add emphasis or flair to a particular moment. Stingers are often used to enhance the listening experience and give structure to the podcast.
Track
In podcasting, a track refers to an individual audio file or recording that forms part of the overall podcast. This could be a recorded interview, a voiceover, music, sound effects, or any other audio element. When editing a podcast, these different tracks can be mixed together, adjusted, and arranged to create the final podcast episode.
Uploading
Uploading a podcast refers to the process of sending your final podcast episode file (usually in MP3 format) to a podcast hosting platform, such as ZenCast. We then distribute the episode to Spotify, Apple Podcasts, etc via your podcast's RSS feed, making the episode available for listeners to download or stream.
USB Microphone
A USB microphone is a mic that connects directly to a device via a USB port, converting analog signals to digital in-built, popular for its ease of use and affordability in podcasting, gaming, and home recording.
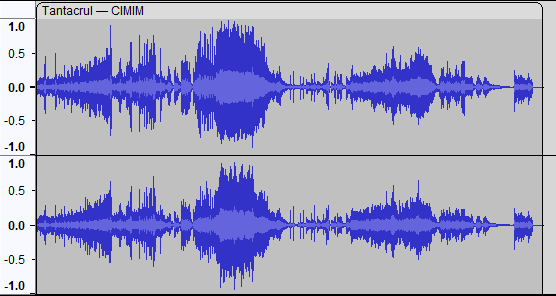
Waveform
A waveform in audio recording is a visual representation of the changes in amplitude (volume) over time. It displays the loudness and quietness of an audio signal at different points in time. Waveforms are used in audio editing software to help identify and manipulate specific parts of an audio track, like removing unwanted noise or adjusting volume levels.
WAV File
A WAV file is a type of digital audio file format. It uses a form of lossless data compression, which means it maintains audio quality but results in larger file sizes compared to lossy formats like MP3. WAV files are often used in professional audio recording and editing due to their high quality, but their large size can make them less practical for casual listening or streaming. We recommend MP3 files for your podcast for the widest compatibility.
XLR Microphone
An XLR microphone is a professional-grade microphone that uses an XLR connector for its output, providing a balanced signal for less noise and enabling the use of long cables without significant signal loss, often used in professional studios and broadcasting.